


We made a cartoon book about infectious diseases. Here’s why.

Developing a Collaborative Community of Practice in Tick Citizen Science
Upon the success of our first Tick Citizen Science online workshop earlier this year, IDAlert facilitated a highly anticipated second Tick Citizen Science Workshop on the 12th November 2025.
Emergence and spread of Hyalomma ticks and Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever in Europe: a systematic review
Mohammed Masud Parvage et al.
Parasites Vectors 18, 436 (2025)
Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever (CCHF) is a severe, often fatal zoonotic disease caused by the CCHF virus (CCHFV). It is primarily transmitted by Hyalomma ticks, which serve as both reservoir and vector. While these ticks are endemic to Asia, Africa, and parts of Europe, recent detections in previously unaffected European regions raise concerns about the potential spread of the disease. This study aims to systematically review the first detections of Hyalomma ticks, CCHFV, and CCHF disease in Europe. The goal is to support surveillance strategies and enhance preparedness for future outbreaks.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-025-07104-3
Importation of the exotic tick Amblyomma geoemydae into Sweden via illegally introduced turtles (Geoemyda spengleri) from Thailand
Giulio Grandi et al.
Veterinary Parasitology: Regional Studies and Reports 63 (2025)
Illegal importation of animals as pets might be followed by the introduction of exotic tick species, potential vectors of pathogens that can have an impact on wildlife and/or domestic animals and on humans. Therefore, permanent measures of surveillance and control on imported reptiles are emphasized. In February 2024, black-breasted leaf turtles (Geoemyda spengleri) (n = 31) were illegally imported into Sweden from Thailand. The turtles were sent by the Swedish Customs Criminal Department West in Gothenburg to a public aquarium and terrarium (Tropicarium, Kolmården, Östergötland county) to be kept in quarantine. At the Tropicarium the turtles were found to be infested by ticks.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vprsr.2025.101304
Automated tick classification using deep learning and its associated challenges in citizen science
Anna Omazic et al.
Sci Rep 15, 24942 (2025)
Lyme borreliosis and tick-borne encephalitis significantly impact public health in Europe, transmitted primarily by endemic tick species. The recent introduction of exotic tick species into northern Europe via migratory birds, imported animals, and travelers highlights the urgent need for rapid detection and accurate species identification. To address this, the Swedish Veterinary Agency launched a citizen science initiative, resulting in the submission of over 15,000 tick images spanning seven species.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-10265-x

IDAlert at Science Week in Blanes, Spain
IDAlert took part of the Science Week organised by CEAB-CSIC in Blanes, Spain
Why the growth of arboviral diseases necessitates a new generation of global risk maps and future projections
Oliver J. Brady et al.
PLoS Comput Biol 21(4): e1012771
Global risk maps are an important tool for assessing the global threat of mosquito and tick-transmitted arboviral diseases. Public health officials increasingly rely on risk maps to understand the drivers of transmission, forecast spread, identify gaps in surveillance, estimate disease burden, and target and evaluate the impact of interventions.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012771

IDAlert at the 9th SOVE International Congress in Chania, Greece
IDAlert took part in the 9th SOVE International Congress, organized by the Society for Vector Ecology (SOVE) and held in Chania, Greece, from 12–17 October 2025.
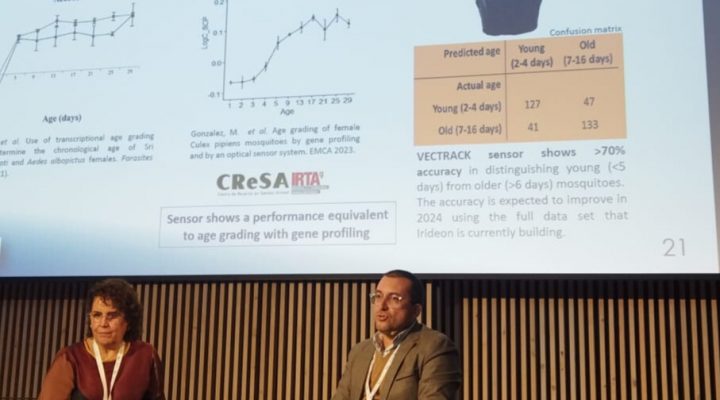
IDAlert at Barcelona Pest Control Innovation Forum
On 6 November, IDAlert partners took part in the Barcelona Pest Control Innovation Forum (BPCIF), presenting two innovative tools that demonstrate the project’s contribution to strengthening public health and vector monitoring.
