

IDAlert at the Thessaloniki International Fair
Thanks to the collaboration of our partner, icddr,b, the Mosquito Alert app has now been introduced in Bangladesh and adapted for local use in Bangla. This deployment empowers communities in Bangladesh to directly participate in mosquito surveillance and control efforts, contributing to early warning systems and targeted interventions.

Turning mosquito troubles into health protection data: Mosquito Alert App launch in Bangladesh
Thanks to the collaboration of our partner, icddr,b, the Mosquito Alert app has now been introduced in Bangladesh and adapted for local use in Bangla. This deployment empowers communities in Bangladesh to directly participate in mosquito surveillance and control efforts, contributing to early warning systems and targeted interventions.

Discover our climate change and health indicators for kids and teens
In 2023, record-breaking global temperatures highlighted the urgent need for climate action to prevent worsening climate-related health impacts. Europe, warming at twice the global average rate, faces significant health threats and unnecessary loss of life. The Lancet Countdown in Europe, established in 2021, aims to drive rapid health-responsive climate actions. Its 2022 report tracked progress using 33 indicators across five domains.
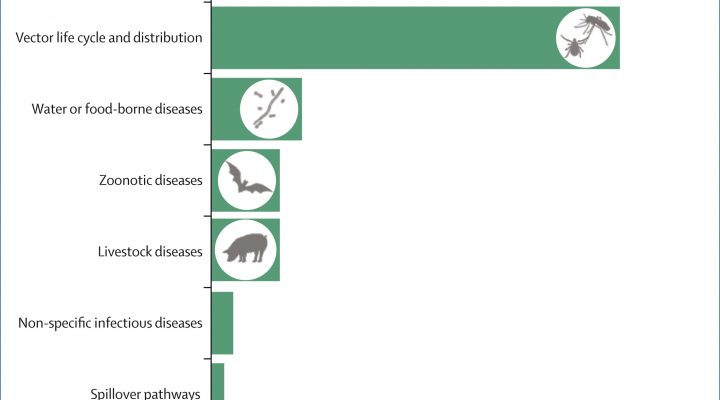
Identifying the climate sensitivity of infectious diseases: a conceptual framework
Alcayna, Tilly et al.
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 0, Issue 0, 101291
Infectious diseases pose a substantial threat to public health, affecting billions and straining health-care systems worldwide. There is growing concern over how anthropogenic climate change might aggravate the global burden of climate-sensitive infectious diseases. In this Personal View, we propose a framework for understanding what makes an infectious disease climate-sensitive.
DOI: 10.1016/j.lanplh.2025.101291

IDAlert discusses mosquito control in Greece
Integrating anticipatory action in disease outbreak preparedness and response in the humanitarian sector
Tilly Alcayna et al.
BMJ Global Health 2025;10:e017721
In the humanitarian sector, anticipatory action entails acting ahead of predicted hazardous events to prevent or mitigate potential impacts and needs. It leverages early warnings to bridge preparedness and response, with a core principle being the provision of ex-ante emergency funding for preagreed early actions. Traditionally applied to extreme climatic events, there is growing interest in integrating anticipatory action into disease outbreak preparedness and response. We present an analytical framework for trigger development for climate-sensitive infectious disease outbreaks based on a review of existing and emerging practices from the Red Cross Red Crescent Movement, United Nations agencies and Médecins Sans Frontières since 2014. We propose that, depending on data availability, there are four broad approaches for trigger development.
DOI: 10.1136/bmjgh-2024-017721

Mobile App and interactive map launched to track the spread of ticks in Sweden
Effects of mosquito-proofing storm drains on adult and larval mosquito abundance: Protocol of the IDAlErt storm drAin randomiSed controlled trial (IDEAS)
Marina Treskova et al.
MethodsX, Volume 14, 2025, 103102
Aedes and Culex mosquitoes, vectors of diseases like dengue and West Nile, breed in urban storm drains with stagnant water, a problem that may worsen in Europe due to climate change. To address this, the Agència de Salut Pública de Barcelona (ASPB) tested structural drain modifications in a randomised controlled trial, assigning 44 drains to either mosquito-proofing or no change and monitoring them weekly from June to November 2023. Outcomes focused on adult mosquito counts and presence of adults and larvae, with results to be analysed using statistical models to assess effectiveness and guide possible city-wide adoption.
DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2024.103102

